Have you ever faced a situation where a part failed, the original supplier was unavailable, and no drawings existed – leaving production on hold?
Many manufacturers in India deal with this daily, especially when parts are imported, obsolete, or not supported by the OEM anymore.
Good news: reverse engineering services help solve this exact problem by rebuilding the part digitally and producing it again with the same fit and function – sometimes even better.
According to Verified Market Reports 2024, the global reverse engineering services market was estimated at USD 1.5 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of about 8.9%.
This blog explains, in the simplest way, how reverse engineering services work in India, step by step, and where different industries are using it today. By the end, you will clearly understand each stage of the process, the deliverables you will receive, and the real business value for OEMs and manufacturers.
In the blog, we explore:
Key Takeaways
- Reverse engineering helps to rebuild a part digitally when original drawings, CAD models, or supplier support are not available.
- It is widely used in India to replace imported parts, support legacy machines, and reduce production downtime.
- The main steps include: NDA and assessment → 3D scanning → Scan-to-CAD reconstruction → engineering analysis → CAD validation → final deliverables → optional prototype and production.
- Typical outputs include 3D CAD models, 2D drawings, BOM, GD&T, CAE reports, and deviation reports, which are ready for manufacturing.
- Industries that benefit most are EV, automotive, aerospace, defence, heavy machinery, medical devices, consumer electronics, renewable energy, and power sectors.
- Real-world results show cost savings, faster delivery, better spare availability, and improved equipment reliability.
- Reverse engineering projects in India can be completed in 3 days to 4 weeks, depending on complexity.
- Costs depend on size, geometry, material, assembly level, tolerance needs, and prototype requirements.
- A case study showed that a capacitor tilt trolley was fully redeveloped locally, resulting in 30% shorter lead time and 25% cost savings.
- Companies prefer reverse engineering in India because it reduces import dependency, lowers downtime, and makes maintenance easier through local spare support.
What Is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering means recreating a 3D CAD model and 2D engineering drawings of an existing part when original technical documents are missing. It focuses on measurement, analysis, and digital reconstruction of the physical component.
When reverse engineering is the right choice
Businesses usually choose it when:
- The part is imported and expensive
- The OEM has discontinued the component
- The drawings are lost or outdated
- A spare part is needed urgently
The design must be improved or localized for India
Typical deliverables you receive
Reverse engineering services in India usually provide:
- 3D CAD model (STEP / IGES / XT / Native formats)
- 2D manufacturing drawing
- Bill of Materials (BOM)
- CAE report
- GD&T tolerance details
- Deviation report (scan vs CAD)
For many OEMs and manufacturers, reverse engineering is now a key method for import replacement, legacy part recovery, and product improvement, especially in sectors like EV, defence, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
The Step-By-Step Reverse Engineering Process in India
Below is the exact workflow followed by professional engineering companies in India.
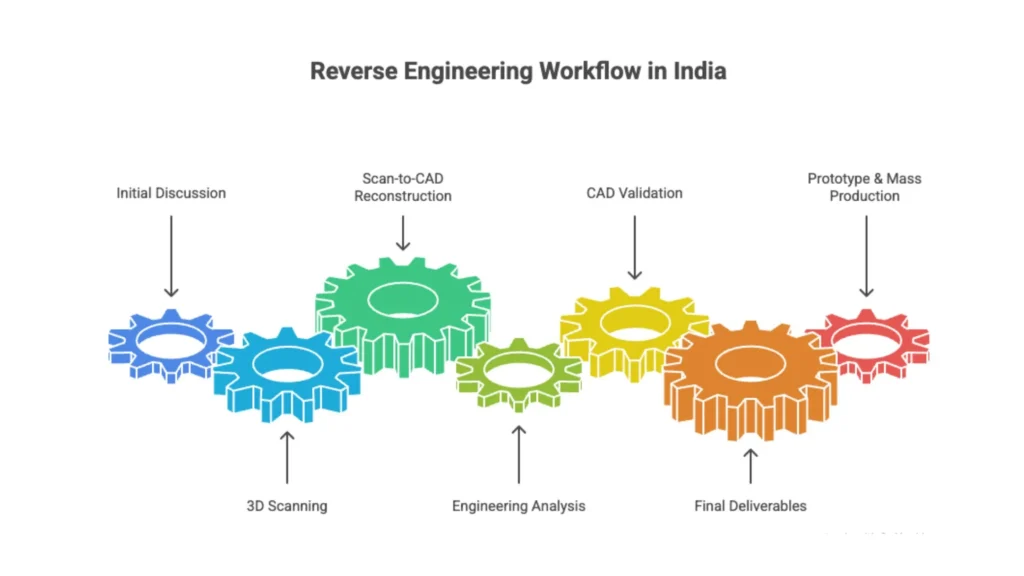
Step 1 – Initial discussion, NDA signing & part assessment
The process begins with a meeting to understand the part, its function, and its performance expectations. Non-Disclosure Agreements are usually signed to protect the client’s intellectual property.
The part is then checked physically to understand dimensions, materials, wear, tolerance sensitivity, and assembly fitment. If needed, the team visits the client location to inspect and measure the component on the machine.
Step 2 – 3D scanning & measurement
Using portable CMM or structured-light 3D scanners, the part is scanned to capture millions of data points within minutes. This generates a point cloud or mesh file, which represents every detail of the part.
Scanning can be done on-site or at the engineering facility, based on urgency and part size.
Step 3 – Scan-to-CAD reconstruction
The scan model is then converted into a fully editable CAD file through either of these:
- Surface modelling – for castings, sheet metal, medical and consumer products
- Parametric modelling – for machined components and assemblies
The recreated CAD gives complete visibility of shape, geometry, holes, profiles, and functional surfaces.
Step 4 – Engineering analysis
At this stage, engineers evaluate:
- GD&T
- Tolerances
- PMI
- Material properties
- Hardness
- FEA/CAE (when required)
If the original part had weak points, the team can adjust tolerances or geometry to avoid repeat failures.
Step 5 – CAD validation
The recreated CAD is checked against the scanned mesh using a deviation report. If the tolerance matches the requirement, the model is approved. If not, adjustments are made.
Step 6 – Final deliverables
The engineering documents are prepared for production, including:
- 3D CAD file
- 2D drawing
- BOM
- GD&T
- CAE/FEA reports (if requested)
These files can be sent to any CNC machine shop, sheet metal supplier, or casting vendor for manufacturing.
Step 7 (Optional) – Prototype & mass production
Many companies in India also support:
- CNC machining of prototypes
- 3D printing
- Casting
- Injection moulding
- Sheet metal
- Forging
This helps move from design to production without depending on multiple vendors — a major reason why OEMs now prefer reverse engineering services in India.
Real Indian Use Cases – Mini Case Scenarios
Below are real-world style cases where reverse engineering services delivered strong results for Indian manufacturers.
| Industry | Problem | Reverse Engineering Approach | Result |
| Automotive EV | Imported charging connector discontinued | 3D scan + CAD rebuild + new mould design | Local production enabled, 42% cost savings |
| Aerospace | Obsolete turbine part with wear | Scan-to-CAD + alloy upgrade | Flight-ready spare delivered without OEM support |
| Defence | Legacy vehicle part without drawings | On-vehicle measurement + CAD + GD&T | Equipment restored and downtime reduced |
| Heavy Machinery | Broken hydraulic block | Reverse model + strength improvement | Longer lifespan and reduced failure rate |
| Medical Devices | Hip implant redesign | Surface scan + CAD + tolerance setup | Better patient fit and lower manufacturing time |
| Consumer Electronics | Imported plastic housing costly | 3D scan + mould-ready design | Cost reduced by ~35% and cycle time improved |
These examples show why reverse engineering case study searches are rising. Many companies prefer local manufacturing instead of waiting for imports or depending on OEMs overseas.
Case Study – Reverse Engineering in the Real World (India)
A strong example of how reverse engineering delivers real value in India comes from an industrial capacitor manufacturing plant that relied on an imported European tilt trolley for capacitor handling.
The trolley was essential for day-to-day operations, but the overseas supplier had long delivery timelines and high costs, which caused frequent production delays.
To overcome this, Venttup carried out complete reverse engineering and local redevelopment of the equipment. The work involved a combination of full system study, physical inspection, 3D reconstruction, and validation trials.
Process followed:
- System study and physical inspection of the trolley
- Creation of 2D technical drawings and 3D CAD models
- Development of a working prototype
- Testing and validation at the customer site
- Final rollout for factory use
Outcome and impact:
- 30% reduction in lead time compared to imports
- 25% cost savings on the equipment
- Faster maintenance because spares became available locally
This case reflects how reverse engineering in India is not used only for part reproduction – it also supports equipment localisation, cost optimisation, and supply-chain stability for OEMs and manufacturers who no longer want to depend on foreign suppliers for critical machinery or spares.
Cost & Timeline Factors in India
Reverse engineering services in India are usually priced based on the following factors:
- Size of the part
- Geometry and tolerance complexity
- Need for surface vs parametric modelling
- Assembly level modelling (if multiple parts)
- Prototype support requirement
- Material analysis
Typical timelines in India
| Complexity | Delivery Time |
| Simple machined parts | 3-7 days |
| Medium complexity | 1-2 weeks |
| Cast / sheet metal / assemblies | 2-4 weeks |
According to a 2024 industrial sourcing survey by Indust2 (India), 77% of Indian manufacturers use reverse engineering to reduce import dependency and improve supply-chain reliability – Indust2 Manufacturing Insights Survey 2024
Reverse engineering services in India also reduce costs by avoiding high Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ), currency fluctuations, and international shipping delays.
Who Should Consider Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is suitable for businesses such as:
- OEMs
- Component manufacturers
- R&D and NPD teams
- Maintenance and overhaul departments
- Aftermarket spare suppliers
- Project and commissioning teams
- Industries working with imported or obsolete components
If your target is lower cost, faster lead time, better control, or local sourcing, reverse engineering is a practical and proven approach.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering has become one of the most practical ways for manufacturers and OEMs to replace imported parts, support legacy equipment, and reduce production downtime. With the right workflow, companies can get production-ready digital files and drawings even when no OEM documents exist.
Many businesses now prefer to work with partners who can take responsibility beyond creating a CAD model. Venttup, a MaaS company supports this complete journey – from initial feasibility and NDA signing to 3D scanning, modelling, tolerance study, and prototype or production support when required. This helps companies avoid working with multiple vendors and ensures that the same engineering intent continues until the component is manufactured.
If you want to replace an imported or obsolete part, reverse engineering services can help you get production-ready CAD files and drawings fast.
You can share part photos or details with Venttup and request an NDA or feasibility check, and the team will respond within 24 – 48 hours.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is reverse engineering legal in India?
Yes, reverse engineering is legal in India. It is commonly used for repair, spare-part replacement, part improvement, and localization of imported components. It becomes a legal problem only if someone copies a branded product for resale with the intention of passing it off as the original brand.
If a company uses reverse engineering to keep their machines running, reduce import dependency, redesign older parts, or improve performance, there is nothing illegal about it.
Do you provide on-site 3D scanning?
Yes. On-site 3D scanning is available in most cases. Portable scanners can be brought directly to factories, power plants, workshops, or project locations to capture the exact dimensions of the component without removing it from the machine. On-site scanning is especially useful when the part is very large, sensitive, installed inside assembly lines, or difficult to transport.
Can reverse engineering be done without drawings?
Yes. Drawings are not required to start reverse engineering. The complete process is actually designed for situations where no technical drawings, 3D models, or OEM data exist. The part itself becomes the reference. Engineers scan the part, measure it, analyse tolerances, and recreate a 3D CAD model and 2D drawing with the same fit and function.
Which industries benefit the most?
Industries that benefit the most from reverse engineering include renewable energy and power, EV and automotive, aerospace and defence, railways and marine, heavy machinery and industrial equipment, Consumer electronics and appliances
and medical devices — especially where downtime is expensive or spare parts are hard to source.
What formats can you deliver?
Most engineering teams can provide all major 3D and 2D file formats used by manufacturing and CAD systems. This may include: STEP, IGES, Parasolid, SLDPRT, PRT, DWG, DXF, and STL.
These formats allow the files to be used directly for CNC machining, 3D printing, mould design, casting, sheet-metal manufacturing, and simulation analysis.
Can you handle complex assemblies?
Yes. Complex assemblies can be scanned and rebuilt digitally. Multiple parts are indexed, organised, and aligned to create a complete 3D assembly model. This is helpful when the part connects with multiple mating components, requires tolerance control, or is part of a larger mechanical system.
Individual components can also be reverse-engineered one by one and then tested virtually for fit and function inside the assembly.